Gallbladder Support Remedy
 The gallbladder is a small muscular sac that sits just under the liver. The gallbladder has the simple task of storing bile produced by the liver. Bile is the main substance responsible for the breaking down of fats and cholesterols in the digestive system. The ingestion of food and especially fats causes the release of a hormone, cholecystokinin, (CCK) which in turn signals the relaxation of the valve at the end of the common bile duct (the sphincter of oddi) and allows the bile to enter the small intestine. It also signals the contraction of the gallbladder which squirts the concentrated liquid bile into the small intestine. There it helps with the emulsification or breakdown of fats from your food. Before a meal, the gallbladder is typically full of bile and about the size of a small pear. After meals, the gallbladder is usually empty and flat, like a deflated balloon.
The gallbladder is a small muscular sac that sits just under the liver. The gallbladder has the simple task of storing bile produced by the liver. Bile is the main substance responsible for the breaking down of fats and cholesterols in the digestive system. The ingestion of food and especially fats causes the release of a hormone, cholecystokinin, (CCK) which in turn signals the relaxation of the valve at the end of the common bile duct (the sphincter of oddi) and allows the bile to enter the small intestine. It also signals the contraction of the gallbladder which squirts the concentrated liquid bile into the small intestine. There it helps with the emulsification or breakdown of fats from your food. Before a meal, the gallbladder is typically full of bile and about the size of a small pear. After meals, the gallbladder is usually empty and flat, like a deflated balloon.
Without adequate bile you do not metabolize your fats well which can result in a deficiency of the fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E and K). You may also have problems digesting the essential fatty acids. In addition to other symptoms you could have trouble utilizing calcium, have dry skin, peeling on the soles of your feet, etc. One way to tell you have trouble digesting fats is if you have excessive burping that starts shortly after eating a meal that has fat in it. You might feel nauseous or experience gas and bloating.
Secondly, bile is a very powerful antioxidant which helps to remove toxins from the liver. The liver filters toxins (bacteria, viruses, drugs or other foreign substances the body doesn't want) and sends them out via bile, which is made in the liver. The path of departure is from the liver through the bile ducts and into the gallbladder or directly into the small intestine where it joins waste matter and leaves through the colon with the feces. A healthy liver produces about a quart to a quart and a half of bile daily. If you have gallbladder problems, you should cleanse your liver and bowel also. Many people with sluggish gallbladders have a tendency towards constipation.
Only three things can go wrong with the gallbladder: inflammation, gallstones and blockage of the ducts. All of these are treated with surgery and removal in the US, but 99% are treatable naturally, without surgery. Severe gall bladder symptoms include: nausea, high temperature, pain in your back between the shoulder blades or pain in your right abdomen.
Fun Facts
- The lack of fat in your diet can bring on a gallbladder attack.
- Allergies / reactions to dairy and casein are often from gallbladder (maybe liver) congestion.
- You could have gallstones, even if you have no symptoms and no gallbladder (they often hide in the liver and an x-ray won't see them)!
Health Conditions
- Gallstones (cholelithiasis) occur when substances in bile crystallize in the gallbladder.
- Cholecystitis (biliary colic) refers to inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Bile obstruction restricts flow of bile from the liver to the gallbladder or from the gallbladder to the intestine.
- Gallstone pancreatitis occurs when an impacted gallstone blocks the ducts that drain the pancreas.
Suggestions To Strengthen
- Avoid animal fats (meat), cheese and fried foods.
- Non organic vitamins, especially calcium, can contribute to gall stones.
- Do a gallstone flush every 3-4 months.
- Forgive old grudges, bitterness leads to gallbladder disease. Write a letter of forgiveness even if the person is no longer living.

 The structure of the female breast is complex. It consists of fat and connective tissue, as well as lobes, lobules, ducts and lymph nodes. Each breast has a number of sections (lobules) that branch out from the nipple. Each lobule holds tiny, hollow sacs called alveoli. The lobules are linked by a network of thin tubes (ducts). If you're breast-feeding, ducts carry milk from the alveoli toward the dark area of skin in the center of the breast (areola). From the areola, the ducts join together into larger ducts ending at the nipple.
The structure of the female breast is complex. It consists of fat and connective tissue, as well as lobes, lobules, ducts and lymph nodes. Each breast has a number of sections (lobules) that branch out from the nipple. Each lobule holds tiny, hollow sacs called alveoli. The lobules are linked by a network of thin tubes (ducts). If you're breast-feeding, ducts carry milk from the alveoli toward the dark area of skin in the center of the breast (areola). From the areola, the ducts join together into larger ducts ending at the nipple. This Remedy helps with all Ovary, Fallopian Tube and egg/follicle cells (fertility). The ovaries are a pair of female reproductive organs. Each ovary is about the size and shape of an almond. They are located in the pelvis, one on each side of the uterus. The ovaries are connected to each other by the Fallopian tubes. The fallopian tubes are two thin tubes, one on each side of the uterus, which help lead the mature egg from the ovaries to the uterus. Some form of blockage, swelling, scar tissue or other conditions of the fallopian tube are a major cause of infertility.
This Remedy helps with all Ovary, Fallopian Tube and egg/follicle cells (fertility). The ovaries are a pair of female reproductive organs. Each ovary is about the size and shape of an almond. They are located in the pelvis, one on each side of the uterus. The ovaries are connected to each other by the Fallopian tubes. The fallopian tubes are two thin tubes, one on each side of the uterus, which help lead the mature egg from the ovaries to the uterus. Some form of blockage, swelling, scar tissue or other conditions of the fallopian tube are a major cause of infertility. Vision begins when light rays are reflected off an object and enter the eyes through the cornea, the transparent outer covering of the eye. The cornea bends or refracts the rays that pass through a round hole called the pupil. The iris, or colored portion of the eye that surrounds the pupil opens and closes (making the pupil bigger or smaller) to regulate the amount of light passing through. The light rays then pass through the lens, which actually changes shape so it can further bend the rays and focus them on the retina at the back of the eye.
Vision begins when light rays are reflected off an object and enter the eyes through the cornea, the transparent outer covering of the eye. The cornea bends or refracts the rays that pass through a round hole called the pupil. The iris, or colored portion of the eye that surrounds the pupil opens and closes (making the pupil bigger or smaller) to regulate the amount of light passing through. The light rays then pass through the lens, which actually changes shape so it can further bend the rays and focus them on the retina at the back of the eye. The esophagus is the tube that delivers food from the mouth to the stomach. When swallowing occurs, food is pushed into the top of the esophagus and is then propelled onwards by waves of circular muscle contraction, called peristalsis. If necessary, this process can defeat gravity! Food, and even liquids, can be swallowed while standing on one's head. Muscles encircling the esophagus at the top and bottom provide sphincters that prevent air from being sucked in during inhalation, and regurgitation of stomach contents.
The esophagus is the tube that delivers food from the mouth to the stomach. When swallowing occurs, food is pushed into the top of the esophagus and is then propelled onwards by waves of circular muscle contraction, called peristalsis. If necessary, this process can defeat gravity! Food, and even liquids, can be swallowed while standing on one's head. Muscles encircling the esophagus at the top and bottom provide sphincters that prevent air from being sucked in during inhalation, and regurgitation of stomach contents.

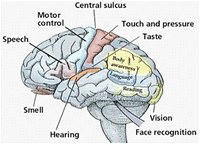 The brain is the most complex organ in the human body, and perhaps the most remarkable. It produces our every thought, action, memory, feeling and experience of the world. This jelly-like mass of tissue, weighing about 3 pounds, contains a staggering one hundred billion nerve cells, or neurons.
The brain is the most complex organ in the human body, and perhaps the most remarkable. It produces our every thought, action, memory, feeling and experience of the world. This jelly-like mass of tissue, weighing about 3 pounds, contains a staggering one hundred billion nerve cells, or neurons.