Dengue fever, also known as breakbone fever, is an infectious tropical disease caused by the dengue virus. Dengue is carried and transmitted by the mosquito. Typically, people infected with dengue virus are asymptomatic (80%) or only have mild symptoms such as an uncomplicated fever. Others have more severe illness (5%), and in a small portion it is life-threatening. The incubation period (time between exposure and onset of symptoms) ranges from 3–14 days with the most common being 4–7 days. Travelers returning from endemic areas are unlikely to have dengue if fever or other symptoms begin more than 14 days after arriving home.
The characteristic symptoms of dengue are sudden-onset fever, headache (typically located behind the eyes), muscle and joint pains, and a rash. The alternative name for dengue, "break-bone fever", comes from the associated muscle and joint pains. The course of infection is divided into three phases: febrile, critical, and recovery.
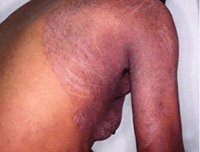
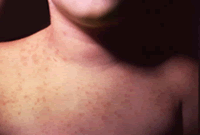
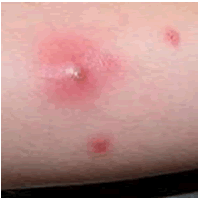
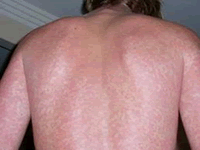
The febrile phase involves high fever, often over 40 °C (104 °F), associated with generalized pain and a headache, usually lasting two to seven days. During this stage, a rash occurs in approximately 50–80% of those with symptoms. If it occurs in the first or second day of symptoms, you will experience flushed skin, later in the course of illness (days 4–7), you develop a measles-like rash. Some petechiae (small red spots that do not disappear when the skin is pressed, which are caused by broken capillaries) can appear at this point, as well as some mild bleeding from the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose. The fever itself is classically biphasic in nature, breaking and then returning for one or two days, although there is wide variation in how often this pattern actually happens.
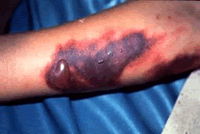
In some people, the disease proceeds to a critical phase, which follows the resolution of the high fever and typically lasts one to two days. During this phase there may be significant fluid accumulation in the chest and abdominal cavity due to increased capillary permeability and leakage. This leads to depletion of fluid from the circulation and decreased blood supply to vital organs. During this phase, organ dysfunction and severe bleeding, typically from the gastrointestinal tract, may occur. Shock (dengue shock syndrome) and hemorrhage (dengue hemorrhagic fever) occur in less than 5% of all cases of dengue. However, those who have previously been infected with other serotypes of dengue virus ("secondary infection") are at an increased risk.
The recovery phase occurs last, with absorption of the leaked fluid into the bloodstream. This usually lasts two to three days. The improvement is often striking, but there may be severe itching and a slow heart rate. During this stage, fluid overload may occur. If it affects the brain, it can cause a reduced level of consciousness or seizures.
Dengue can occasionally affect several other body systems, causing its own set of symptoms in addition to the classic dengue symptoms. A decreased level of consciousness occurs in 0.5–6% of severe cases, which is attributable either to infection of the brain by the virus or indirectly as a result of impairment of vital organs, for example, the liver. Other neurological disorders have been reported in the context of dengue, such as transverse myelitis and Guillain-Barré syndrome. Infection of the heart and acute liver failure are among the more rare complications.
The incidence of dengue fever has increased dramatically since the 1960s, with around 50–100 million people infected annually. If you are traveling to an area where you may be exposed to this condition, consider the Dengue Remedy along with the Mosquito Detox remedy.