Histoplasma
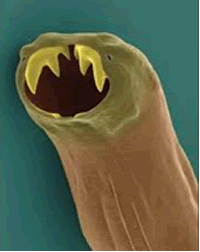
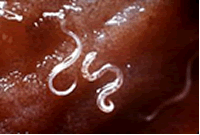
Two species of hookworms commonly infect humans, they are Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus. Hookworms are round worms that generally live in the small intestine of their host. They are generally associated with dogs, cats and humans. Hookworms are thought to infect more than 600 million people worldwide. Ancylostomiasis, also known by several other names, is the disease caused when large numbers of A. duodenale hookworms produce an iron deficiency anemia by sucking blood from the host's intestinal walls.
The worms suck blood voraciously and damage the mucosa of the intestine. However, the blood loss in the bowel movement is not visibly apparent.
Hookworms are a leading cause of maternal and child morbidity in the developing countries of the tropics and subtropics. In susceptible children, hookworms cause intellectual, cognitive and growth retardation. In newborns they cause intrauterine growth retardation, premature birth, and low birth weight when born to infected mothers.
Hookworm eggs are passed in the feces of an infected person. If the infected person or animal defecates outside or if the feces of an infected person or animal are used as fertilizer, eggs are deposited in the soil. The eggs mature and hatch, releasing larvae. The larvae mature into a form that can penetrate the skin of humans. Hookworm infection is mainly acquired by walking barefoot on contaminated soil. One kind of hookworm can also be transmitted through the ingestion of larvae. The moral of the story here is to never walk bare foot where animals may have pooped because you don't know which ones are infected and which are not.
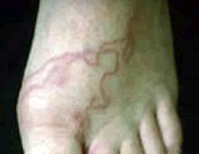
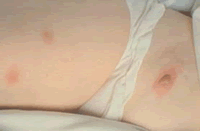
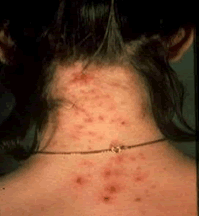
Larval invasion of the skin might give rise to intense, local itching, usually on the foot or lower leg, which can advance to lesions that look like insect bites, can blister ("ground itch"), and last for a week or more. Animal hookworm larvae on penetrating humans may produce a creeping eruption called cutaneous larva migrans (see photo). The larvae migrate in tortuous tunnels in between layers of the skin, causing serpigenous vesicular lesions.
Hookworm infection is generally considered to be asymptomatic, but as Norman Stoll described in 1962, hookworm is an extremely dangerous infection because its damage is "silent and insidious." There are general symptoms that an individual may experience soon after infection. Ground-itch, which is an allergic reaction at the site of parasitic penetration and entry, is common in patients infected with N. americanus. Additionally, cough and pneumonitis may result as the larvae begin to break into the alveoli and travel up the trachea. Once the larvae reach the small intestine of the host and begin to mature, the infected individual will suffer from diarrhea and other gastrointestinal discomfort. However, the "silent and insidious" symptoms referred to by Stoll are related to chronic, heavy-intensity hookworm infections. Major morbidity associated with hookworm is caused by intestinal blood loss, iron deficiency anemia, and protein malnutrition. They result mainly from adult hookworms in the small intestine ingesting blood, rupturing erythrocytes, and degrading hemoglobin in the host. This long-term blood loss can manifest itself physically through facial and peripheral edema. Eosinophilia and pica caused by iron deficiency anemia are also experienced by some hookworm-infected patients.
With advancing movement of the larvae, the rear portions of the lesions become dry and crusty. The lesions are typically extremely pruritic (itchy). Coughing, chest pain, wheezing, and fever will sometimes be experienced by people who have been exposed to very large numbers of larvae. Epigastric pains, indigestion, nausea, vomiting, constipation, and diarrhea can occur early or in later stages as well, although gastrointestinal symptoms tend to improve with time. Signs of advanced severe infection are anemia and protein deficiency, including emaciation, cardiac failure and abdominal distension with ascites (fluid buildup).