Breast Support Remedy
 The structure of the female breast is complex. It consists of fat and connective tissue, as well as lobes, lobules, ducts and lymph nodes. Each breast has a number of sections (lobules) that branch out from the nipple. Each lobule holds tiny, hollow sacs called alveoli. The lobules are linked by a network of thin tubes (ducts). If you're breast-feeding, ducts carry milk from the alveoli toward the dark area of skin in the center of the breast (areola). From the areola, the ducts join together into larger ducts ending at the nipple.
The structure of the female breast is complex. It consists of fat and connective tissue, as well as lobes, lobules, ducts and lymph nodes. Each breast has a number of sections (lobules) that branch out from the nipple. Each lobule holds tiny, hollow sacs called alveoli. The lobules are linked by a network of thin tubes (ducts). If you're breast-feeding, ducts carry milk from the alveoli toward the dark area of skin in the center of the breast (areola). From the areola, the ducts join together into larger ducts ending at the nipple.
Spaces around the lobules and ducts are filled with fat, ligaments and connective tissue. The amount of fat in your breasts largely determines their size although the actual milk-producing structures are nearly the same in all women. Female breast tissue is also sensitive to cyclic changes in hormone levels. Younger women might have denser and less fatty breast tissue than do older women who've gone through menopause.
Muscles lie underneath the breasts, separating them from your ribs. Oxygen and nutrients travel to breast tissue through the blood in your arteries and capillaries (thin, fragile blood vessels). While there is no muscle tissue in the breast, it has been proven that all exercises that include the pectoral muscles will help keep the breasts from being affected by gravity. The overall health of the pectoral muscles are controlled by the health of the stomach and liver, so keeping those organs healthy is critical to breast tissue staying lifted.
Fun Facts
- The average breast weighs 1.1 lbs and contains 4-5% of the body's fat.
- The average breast size in America is currently a 36C, although 15 years ago it was a 34B.
- Breast milk tastes sweeter than cow's milk.
- Smokers will have more droop to their breasts than non-smokers, because the chemicals in cigarettes break down the body's elastin.
Health Conditions
- Mammograms, yes, are a health risk! The pressure applied is traumatic for breast tissue and can encourage a non-cancerous area to become cancerous because of the trauma. Use a Thermogram if you desire a medical breast exam. Click here for more info.
- Breast cysts are fluid-filled sacs within your breast.
- Breast lumps are generally fluid-filled sac or swelling of a lymph node.
- Fibrocystic Breast is when the breast tissue becomes lumpy, generally caused by a need for Progesterone.
Suggestions To Strengthen
- Avoid birth control. The extra estrogen in the body highly contributes to breast conditions and even cancer.
- Exercise regularly, it keeps the lymphatic system draining which is critical for breast health.
- Most breast lumps are congested lymph nodes, often caused by the aluminum and pore clogging agents in antiperspirants. Consider a natural deodorant.
- A mammogram puts so much pressure on a lump in the breast, the trauma can cause cancer in the lump that was not previously there. If you want a breast scan look into Thermograms rather than mammograms.
- Make sure you feel loved and nurtured (loved, cared for, special, protected) by your spouse. This is VERY important.
Complete support remedy for Female Breast and related functions
Complete support remedy for Thyroid and related functions
Complete support remedy for Small Intestine and related functions
Provides support and healing for conditions of the large intestine


 This Remedy helps with all Ovary, Fallopian Tube and egg/follicle cells (fertility). The ovaries are a pair of female reproductive organs. Each ovary is about the size and shape of an almond. They are located in the pelvis, one on each side of the uterus. The ovaries are connected to each other by the Fallopian tubes. The fallopian tubes are two thin tubes, one on each side of the uterus, which help lead the mature egg from the ovaries to the uterus. Some form of blockage, swelling, scar tissue or other conditions of the fallopian tube are a major cause of infertility.
This Remedy helps with all Ovary, Fallopian Tube and egg/follicle cells (fertility). The ovaries are a pair of female reproductive organs. Each ovary is about the size and shape of an almond. They are located in the pelvis, one on each side of the uterus. The ovaries are connected to each other by the Fallopian tubes. The fallopian tubes are two thin tubes, one on each side of the uterus, which help lead the mature egg from the ovaries to the uterus. Some form of blockage, swelling, scar tissue or other conditions of the fallopian tube are a major cause of infertility. Vision begins when light rays are reflected off an object and enter the eyes through the cornea, the transparent outer covering of the eye. The cornea bends or refracts the rays that pass through a round hole called the pupil. The iris, or colored portion of the eye that surrounds the pupil opens and closes (making the pupil bigger or smaller) to regulate the amount of light passing through. The light rays then pass through the lens, which actually changes shape so it can further bend the rays and focus them on the retina at the back of the eye.
Vision begins when light rays are reflected off an object and enter the eyes through the cornea, the transparent outer covering of the eye. The cornea bends or refracts the rays that pass through a round hole called the pupil. The iris, or colored portion of the eye that surrounds the pupil opens and closes (making the pupil bigger or smaller) to regulate the amount of light passing through. The light rays then pass through the lens, which actually changes shape so it can further bend the rays and focus them on the retina at the back of the eye. The esophagus is the tube that delivers food from the mouth to the stomach. When swallowing occurs, food is pushed into the top of the esophagus and is then propelled onwards by waves of circular muscle contraction, called peristalsis. If necessary, this process can defeat gravity! Food, and even liquids, can be swallowed while standing on one's head. Muscles encircling the esophagus at the top and bottom provide sphincters that prevent air from being sucked in during inhalation, and regurgitation of stomach contents.
The esophagus is the tube that delivers food from the mouth to the stomach. When swallowing occurs, food is pushed into the top of the esophagus and is then propelled onwards by waves of circular muscle contraction, called peristalsis. If necessary, this process can defeat gravity! Food, and even liquids, can be swallowed while standing on one's head. Muscles encircling the esophagus at the top and bottom provide sphincters that prevent air from being sucked in during inhalation, and regurgitation of stomach contents.


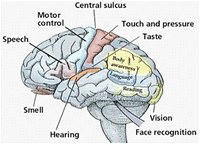 The brain is the most complex organ in the human body, and perhaps the most remarkable. It produces our every thought, action, memory, feeling and experience of the world. This jelly-like mass of tissue, weighing about 3 pounds, contains a staggering one hundred billion nerve cells, or neurons.
The brain is the most complex organ in the human body, and perhaps the most remarkable. It produces our every thought, action, memory, feeling and experience of the world. This jelly-like mass of tissue, weighing about 3 pounds, contains a staggering one hundred billion nerve cells, or neurons.