 Human papillomaviruses (HPV) establish productive infections either in keratinocytes of the skin (outermost layer of the skin, causing warts) or in mucous membranes, as in the case of HPV. HPV is the most frequent sexually transmitted disease in the world!
Human papillomaviruses (HPV) establish productive infections either in keratinocytes of the skin (outermost layer of the skin, causing warts) or in mucous membranes, as in the case of HPV. HPV is the most frequent sexually transmitted disease in the world!
These viruses are responsible for common warts, plantar warts, flat warts and possibly the cause of many skin tags. More than 30 to 40 types of HPV are typically transmitted through sexual contact and infect the anal-genital region. Some sexually transmitted HPV types may cause genital warts. Persistent infection with "high-risk" HPV types — different from the ones that cause skin warts — may progress to precancerous lesions and invasive cancer. HPV infection is a cause of nearly all cases of cervical cancer.
Over 120 HPV types have been identified and are referred to by number. Types 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, and 59 are considered the "high-risk" sexually transmitted HPVs and may lead to the development of cancers and other diseases. Following is a list of various conditions/disease and their associated HPV.
- Common warts: 2, 7
- Plantar warts: 1, 2, 4, 63
- Flat warts: 3, 10
- Anal-genital warts: 6, 11, 42, 44 and others
- Genital cancers, Highest risk: 16, 18, 31, 45, Other high-risk: 33, 35, 39, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, Possible high-risk: 26, 53, 66, 68, 73, 82
- Epidermodysplasia verruciformis: more than 15 types
- Focal epithelial hyperplasia (oral): 13, 32
- Oral papillomas: 6, 7, 11, 16, 32
- Oropharyngeal cancer: 16
- Laryngeal papillomatosis: 6,11
Although genital HPV types can be transmitted from mother to child during birth, the appearance of genital HPV-related diseases in newborns is rare. Perinatal transmission of HPV types 6 and 11 can result in the development of juvenile-onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (JORRP). JORRP is very rare, with rates of about 2 cases per 100,000 children in the United States. Although JORRP rates are substantially higher if a woman presents with genital warts at the time of giving birth, the risk of JORRP in such cases is still less than 1%.
At least 40 identified HPV types infect the genital tract. If a college woman has at least one different partner per year for four years, the probability that she will leave college with an HPV infection is greater than 85%. Condoms do not completely protect from the virus because the areas around the genitals including the inner thigh area are not covered, thus exposing these areas to the infected person's skin.
Because HPV is considered a precursor for cancer, preventative surgery for HPV can cause infertility and is completely unnecessary, even though it is what modern medicine advocates.





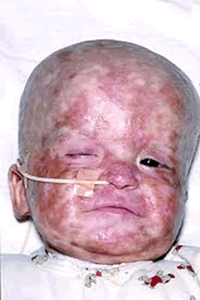
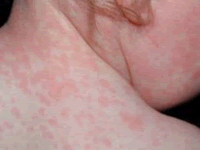
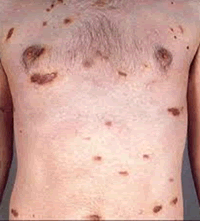
 Hepatitis A is caused by eating food and drinking water infected with a virus called HAV. It can also be caused by anal-oral contact during sex. Tens of millions of individuals worldwide are estimated to be infected with Hep A each year. Hepatitis A infection causes no clinical signs and symptoms in over 90% of infected children. Although it can cause swelling and inflammation in the liver, it doesn't generally lead to chronic, or life long, disease. Almost everyone who gets hepatitis A has a full recovery. Early symptoms of hepatitis A infection can be mistaken for influenza, but some sufferers, especially children, exhibit no symptoms at all. Symptoms typically appear 2 to 6 weeks, (the incubation period), after the initial infection. They usually last less than 2 months, although some people can be ill for as long as 6 months. Symptoms include: Fatigue, Fever, Abdominal pain, Nausea, Appetite loss, and Jaundice (a yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes). Bile is removed from the blood stream and excreted in urine, giving it a dark amber color and likely a Clay-colored feces.
Hepatitis A is caused by eating food and drinking water infected with a virus called HAV. It can also be caused by anal-oral contact during sex. Tens of millions of individuals worldwide are estimated to be infected with Hep A each year. Hepatitis A infection causes no clinical signs and symptoms in over 90% of infected children. Although it can cause swelling and inflammation in the liver, it doesn't generally lead to chronic, or life long, disease. Almost everyone who gets hepatitis A has a full recovery. Early symptoms of hepatitis A infection can be mistaken for influenza, but some sufferers, especially children, exhibit no symptoms at all. Symptoms typically appear 2 to 6 weeks, (the incubation period), after the initial infection. They usually last less than 2 months, although some people can be ill for as long as 6 months. Symptoms include: Fatigue, Fever, Abdominal pain, Nausea, Appetite loss, and Jaundice (a yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes). Bile is removed from the blood stream and excreted in urine, giving it a dark amber color and likely a Clay-colored feces. Echo (Enteric Cytopathic Human Orphan) viruses are found in the gastrointestinal tract (hence it being part of the enterovirus genus) and exposure to these viruses causes other opportunistic infections and diseases. Echovirus is highly infectious, and its primary target is children. The echovirus is among the leading causes of acute febrile illness in infants and young children, and is the most common cause of aseptic meningitis. Infection of an infant with this virus following birth may cause severe systemic diseases and is associated with high infant mortality rates. The echovirus can mimic symptoms caused by other common bacterial and viral infections.
Echo (Enteric Cytopathic Human Orphan) viruses are found in the gastrointestinal tract (hence it being part of the enterovirus genus) and exposure to these viruses causes other opportunistic infections and diseases. Echovirus is highly infectious, and its primary target is children. The echovirus is among the leading causes of acute febrile illness in infants and young children, and is the most common cause of aseptic meningitis. Infection of an infant with this virus following birth may cause severe systemic diseases and is associated with high infant mortality rates. The echovirus can mimic symptoms caused by other common bacterial and viral infections. Enteroviruses are a genus of viruses associated with several human and mammalian diseases. On the basis of their pathogenesis in humans and animals, the enteroviruses were originally classified into four groups, all of which (along with all serotypes) are included in the Enterovirus Detox Remedy: polioviruses, Coxsackie A viruses (CA), Coxsackie B viruses (CB), and Echoviruses.
Enteroviruses are a genus of viruses associated with several human and mammalian diseases. On the basis of their pathogenesis in humans and animals, the enteroviruses were originally classified into four groups, all of which (along with all serotypes) are included in the Enterovirus Detox Remedy: polioviruses, Coxsackie A viruses (CA), Coxsackie B viruses (CB), and Echoviruses.